A block has four fields, or primary attributes:. SHA is a cryptographic hash algorithm that produces a unique bit alphanumeric hash value for any given input, and that is the unique feature of this cryptographic algorithm: Whatever input you give, it will always produce a bit hash. Bitcoin mining is the process of verifying bitcoin transactions and recording them in the public blockchain ledger. In blockchain, the transactions are verified by bitcoin users, so basically the transactions have to be verified by the participants of the network. Those who have the required hardware and computing power are called miners.
We will talk more about them later, but the important concept to understand here is that there is nothing like a centralized body—a regulatory body, a governing body, a bank—to make bitcoin transactions go through. Any user with mining hardware and Internet access can be a participant and contribute to the mining community. The process is solved based on a difficult mathematical puzzle called proof of work.
The proof of work is needed to validate the transaction and for the miner to earn a reward. All the miners are completing amongst themselves to mine a particular transaction; the miner who first solves the puzzle gets the reward. Miners are the network participants who have the necessary hardware and computing power to validate the transactions.
To understand bitcoin mining, you have to first understand the three major concepts of blockchain. In the bitcoin network, as mentioned, users called miners are trying to solve a mathematical puzzle. The puzzle is solved by varying a nonce that produces a hash value lower than a predefined condition, which is called a target. As of today, Bitcoin miners who solve a puzzle get a reward of Once a block is added to the blockchain, the bitcoins associated with the transactions can be spent and the transfer from one account to the other can be made.
To generate the hash, Bitcoin miners use the SHA hashing algorithm and define the hash value. If it is less than the defined condition the target , then the puzzle is deemed to be solved. If not, then they keep modifying the nonce value and repeat the SHA hashing function to generate the hash value again, and they keep doing this process until they get the hash value that is less than the target.
To do that, what would the steps be? First, transaction data is shared with bitcoin users from the memory pool. The transaction sits in an unmined pool of memory transactions. In a memory pool, unconfirmed transactions wait until they are verified and included in a new block. Bitcoin miners compete to validate the transaction using proof of work. The miner who solves the puzzle first shares the result across the other nodes. Once the block has been verified, the nonce has been generated, then the nodes will start granting their approval. If maximum nodes grant their approval, the block becomes valid and is added to the blockchain.
The miner who has solved the puzzle will also receive a reward of The 10 bitcoins for which the transaction was initiated now will be transferred from Beyonce to Jennifer. In proof of work, a predefined condition the target is adjusted for every 2, blocks, which is approximately every 14 days. The average time to mine a block is 10 minutes, and to keep the time frame for block generation within 10 minutes, the target keeps adjusting itself.
The difficulty of the puzzle changes depending on the time it takes to mine a block. This is how the difficulty of a block is generated: It is the hash target of the first block divided by the hash target of the current block. This is the difficulty being changed after every 2, blocks, so basically it is very hard to generate the proof of work—but it is very easy for the miners to verify once someone have solved the puzzle. And once the majority of the miners reach a consensus, the block gets validated and added to the blockchain.
That is, when a user makes public transactions, their unique code called a public key , is recorded on the blockchain, rather than their personal information. Once a transaction is recorded, its authenticity must be verified by the blockchain network.
Block (Bitcoin Block)
Thousands of computers on the blockchain rush to confirm that the details of the purchase are correct. After a computer has validated the transaction, it is added to the blockchain block. Each block on the blockchain contains its own unique hash, along with the unique hash of the block before it. This discrepancy makes it extremely difficult for information on the blockchain to be changed without notice. Most blockchains are entirely open-source software.
This means that anyone and everyone can view its code.
BlockchainBlockData (for Bitcoin)—Wolfram Language Documentation
This gives auditors the ability to review cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin for security. Because of this, anyone can suggest changes or upgrades to the system. If a majority of the network users agree that the new version of the code with the upgrade is sound and worthwhile then Bitcoin can be updated. Perhaps the most profound facet of blockchain and Bitcoin is the ability for anyone, regardless of ethnicity, gender, or cultural background, to use it.
According to the world bank there are nearly 2 billion adults that do not have bank accounts or any means of storing their money or wealth. These people often earn little money that is paid in physical cash.
- Chapter 7. The Blockchain.
- usb wallet for bitcoin.
- Block Chain — Bitcoin.
- Block (Bitcoin Block) Definition.
- bitcoin cash fork block height.
- Bitcoin Transactions Explained.
They then need to store this physical cash in hidden locations in their homes or places of living leaving them subject to robbery or unnecessary violence. Keys to a bitcoin wallet can be stored on a piece of paper, a cheap cell phone, or even memorized if necessary.
For most people, it is likely that these options are more easily hidden than a small pile of cash under a mattress. Blockchains of the future are also looking for solutions to not only be a unit of account for wealth storage, but also to store medical records, property rights, and a variety of other legal contracts. While there are significant upsides to the blockchain, there are also significant challenges to its adoption. The roadblocks to the application of blockchain technology today are not just technical. The real challenges are political and regulatory, for the most part, to say nothing of the thousands of hours read: money of custom software design and back-end programming required to integrate blockchain to current business networks.
Here are some of the challenges standing in the way of widespread blockchain adoption. Although blockchain can save users money on transaction fees, the technology is far from free. In the real world, the power from the millions of computers on the bitcoin network is close to what Denmark consumes annually. Despite the costs of mining bitcoin, users continue to drive up their electricity bills in order to validate transactions on the blockchain.
When it comes to blockchains that do not use cryptocurrency, however, miners will need to be paid or otherwise incentivized to validate transactions. Some solutions to these issues are beginning to arise. For example, bitcoin mining farms have been set up to use solar power, excess natural gas from fracking sites, or power from wind farms. Bitcoin is a perfect case study for the possible inefficiencies of blockchain.
Although other cryptocurrencies such as Ethereum perform better than bitcoin, they are still limited by blockchain.
Legacy brand Visa, for context, can process 24, TPS. Solutions to this issue have been in development for years. There are currently blockchains that are boasting over 30, transactions per second. While confidentiality on the blockchain network protects users from hacks and preserves privacy, it also allows for illegal trading and activity on the blockchain network. The website allowed users to browse the website without being tracked using the Tor browser and make illegal purchases in Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies.
Current U. This system can be seen as both a pro and a con. It gives anyone access to financial accounts but also allows criminals to more easily transact. Many have argued that the good uses of crypto, like banking the unbanked world, outweigh the bad uses of cryptocurrency, especially when most illegal activity is still accomplished through untraceable cash. Many in the crypto space have expressed concerns about government regulation over cryptocurrencies.
While it is getting increasingly difficult and near impossible to end something like Bitcoin as its decentralized network grows, governments could theoretically make it illegal to own cryptocurrencies or participate in their networks. Over time this concern has grown smaller as large companies like PayPal begin to allow the ownership and use of cryptocurrencies on its platform. With many practical applications for the technology already being implemented and explored, blockchain is finally making a name for itself at age twenty-seven, in no small part because of bitcoin and cryptocurrency.
As a buzzword on the tongue of every investor in the nation, blockchain stands to make business and government operations more accurate, efficient, secure, and cheap with fewer middlemen. Blockchain Technology. Your Privacy Rights. To change or withdraw your consent choices for Investopedia.
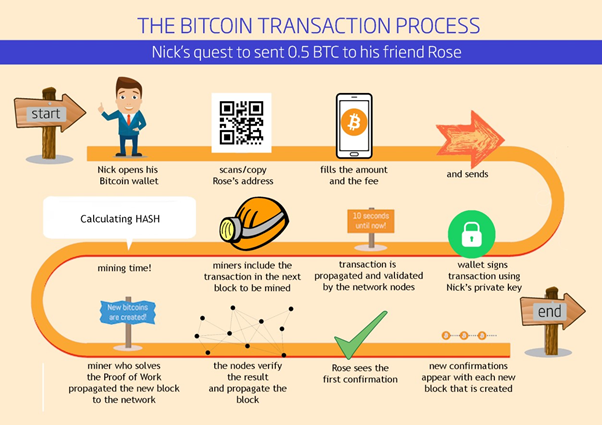
A sample bitcoin transaction
At any time, you can update your settings through the "EU Privacy" link at the bottom of any page. These choices will be signaled globally to our partners and will not affect browsing data. We and our partners process data to: Actively scan device characteristics for identification. I Accept Show Purposes. Your Money. Personal Finance.
Your Practice. Popular Courses. Part Of. Blockchain Basics. Blockchain History.
Blockchain and Industry. Blockchain and the Economy. Blockchain and Banking. Blockchain ETFs. Table of Contents Expand.
Navigation menu
What is Blockchain? Storage Structure. Is Blockchain Secure? Bitcoin vs. Blockchain vs. How is Blockchain Used? Advantages and Disadvantages of Blockchain.